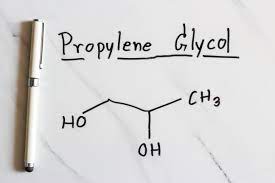
Propylene glycol and ethylene glycol are two closely related compounds that are used extensively in various industries. They both have similar chemical properties but differ significantly in terms of their uses and applications. In this article, we will be exploring the differences between propylene glycol and ethylene glycol to help you understand how they can each be used and which one is best for your specific needs.
PG vs EG
Propylene Glycol (PG) and Ethylene Glycol (EG) are both organic compounds that are widely used in various industries. PG is a clear, colorless, and odorless liquid that is commonly used as a humectant, solvent, and carrier for flavors and fragrances in the food and cosmetic industry. On the other hand, EG is also a clear, colorless liquid but has a slightly sweet taste. It is mainly used as an antifreeze agent in automotive coolants.
One of the primary differences between PG and EG is their toxicity levels. While PG has low toxicity levels to humans and animals, EG can be highly toxic when ingested or absorbed through the skin. In fact, EG poisoning can lead to severe health complications such as kidney failure and even death. Therefore, it’s essential always to handle EG with care.
Another difference between PG vs.EG lies in their freezing points- PG has a relatively high freezing point compared to EG. This makes it unsuitable for use as an automotive coolant but ideal for use in food preservation systems that require low temperatures like refrigerators or freezers. Conversely,Ethylene glycol’s lower freezing point makes it perfect for use as antifreeze in automotive cooling systems since it prevents engine coolant from freezing during cold weather conditions while maintaining its fluidity at high temperatures during summer months.
Properties: Differences
Propylene glycol and ethylene glycol are both organic compounds that have a wide range of industrial applications. Although these two chemicals share some similarities, they also have distinct differences that set them apart.
One key difference between propylene glycol and ethylene glycol is their chemical structure. Propylene glycol consists of three carbon atoms, while ethylene glycol contains two carbon atoms. This structural difference leads to variations in their physical properties such as boiling points and viscosity.
Another significant distinction between the two is their toxicity levels. Ethylene glycol is highly toxic and can result in fatal consequences if ingested, while propylene glycol is considered safe for use in food products, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals due to its low toxicity levels.
Both propylene and ethylene glycols are used as antifreeze agents but for different purposes because of the difference in their chemical properties. Propylene Glycol has a lower freezing point than water which makes it an ideal ingredient for antifreezes used mainly in cooling systems for HVAC equipment or engines that don’t operate below -50°C. Conversely, Ethylene Glycol has a much lower freezing point making it an excellent option when mixed with water providing protection against freezing down to temperatures around -70°C commonly found on automotive engines during winter times.
Health Effects: Risks

Propylene glycol and ethylene glycol are two types of chemicals often used in various industries, including the food, pharmaceuticals, and automotive sectors. However, while propylene glycol is considered safe for human consumption and use, ethylene glycol poses a significant health risk.
Ethylene glycol is highly toxic to humans and animals when ingested or absorbed through the skin. It can cause severe gastrointestinal issues such as vomiting, stomach pain, and diarrhea. Moreover, it can lead to kidney damage or failure and even death if not treated immediately.
On the other hand, propylene glycol is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the U.S Food & Drug Administration (FDA). It is commonly used in numerous consumer products as it acts as a solvent for flavors and colors in food products. Propylene Glycol has low toxicity levels compared to Ethylene Glycol making it relatively safer for use in humans.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between propylene glycol vs. ethylene glycols is crucial to avoid any potential risks associated with these chemicals’ usage. While propyene Glycols are relatively safe for humans with minimal side effects when consumed moderately , ethyene Glycols should be avoided at all costs due to their high toxicity levels that pose significant health risks if not handled with caution.
Applications: Uses
Propylene glycol and ethylene glycol are both types of organic compounds commonly used in a wide variety of applications. Propylene glycol, also known as 1,2-propanediol, is a colorless and odorless liquid that is widely used as an antifreeze and solvent in various industrial processes. It is also commonly found in many everyday products such as cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and food additives. Additionally, propylene glycol has been approved by the FDA for use as an additive in human food.
On the other hand, ethylene glycol is a colorless and sweet-tasting liquid that is primarily used as an antifreeze in automotive cooling systems due to its ability to lower the freezing point of water. However, unlike propylene glycol which has low toxicity levels and is safe for human consumption at low doses, ethylene glycol can be extremely toxic if ingested by humans or animals.
Therefore, when it comes to choosing between propylene glycol vs. ethylene glycol for various applications such as antifreeze or solvent usage, it’s important to consider their toxicity levels carefully.
Environmental Impact: Pollution
Propylene Glycol (PG) and Ethylene Glycol (EG) are two common ingredients found in antifreeze fluids. Although both of these compounds have the ability to lower the freezing point of water, they differ significantly in their environmental impact. EG is highly toxic and poses a serious threat to humans, animals, and plants if ingested or exposed through skin contact. In contrast, PG is considered non-toxic and has been approved for use in food, pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.
When it comes to environmental impact, EG can be especially damaging if it enters the soil or water systems. This compound can contaminate groundwater sources which can cause harm to aquatic life as well as pollute drinking water supplies. Exposure to EG can also result in long-term health problems such as kidney failure or neurological damage.
On the other hand, PG does not pose a significant risk to the environment when used responsibly. This compound has a low toxicity level which means that it doesn’t have harmful effects on wildlife or aquatic habitats like EG does. Additionally, PG is biodegradable which makes it an environmentally-friendly option compared to its toxic counterpart.
Cost Comparison: Prices
When it comes to comparing the cost of propylene glycol and ethylene glycol, several factors come into play. Ethylene glycol is usually less expensive than propylene glycol because it is produced in larger quantities and has a broader range of uses. It is commonly used as an antifreeze agent in automobiles, airplanes, and other machines that require cooling systems.
On the other hand, propylene glycol is generally more expensive than ethylene glycol due to its higher purity levels and more stringent manufacturing processes. Propylene glycol is often used in food products, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals since it poses a lower risk of toxicity compared to ethylene glycol.
Despite the cost differences between these two chemicals, both have their unique advantages depending on their intended use. Therefore, before making a purchasing decision based solely on price alone, it’s essential to consider the specific application of each chemical carefully.
Conclusion: Summary
In conclusion, it is clear that propylene glycol and ethylene glycol have distinct differences in their chemical properties and potential uses. While propylene glycol is a safer alternative for use in food, medicine, and cosmetics due to its low toxicity levels, ethylene glycol is commonly used as a coolant in automotive engines. It’s important to note that both chemicals should be handled with caution and stored properly to prevent accidental ingestion or exposure.
In addition, propylene glycol has the ability to dissolve water-soluble substances which make it ideal for use in pharmaceuticals as a carrier for active ingredients. On the other hand, ethylene glycol has higher boiling points making it suitable for industrial applications like refrigeration systems because of its better thermal stability.
In summary, when choosing between these two chemicals, it’s essential to consider their intended purpose carefully. Propylene glycol might be an excellent option if you’re looking for a safe solvent while Ethylene Glycols are more suited towards industrial applications where high-temperature stability is crucial. Regardless of which one you choose; always remember to handle them with care and store them appropriately.